Centrifugal Pump Problems & Answers
Centrifugal Pump Problems & Answers white paper
By Mike Sondalini

If you have a centrifugal pump problem, the odds are Mike Sondalini has included the solution in this very detailed Pump PDF white paper - "Centrifugal Pump Problems & Answers" (Revision III). Mike goes through the problem-solving steps in detail with his own experiences and research. Although this eBook of white papers primarily focuses on the centrifugal pump, many of the solutions are applicable to pumps in general. 46 pages
With over 50 sections, we can only list a few below. Some of the areas of discussion are flow, mechanical seal, bearings, rotor, cavitations, liquid density, couplings, vibration isolation, fan, metal corrosion, impeller, balancing, alignment and even the effects on electric motors.
Centrifugal Pumps Problems & Answers - Contents:
Changing the service duty of a pump
When centrifugal pumps are modified to perform a different duty the new service head, flow, and motor power characteristics are calculated from the Similarity Laws.
Flange bolting-up practices
Bolts and gaskets behave like springs and unless flange bolts and nuts are properly tensioned the flange will leak. The correct tightening torque depends on bolt diameter, the material of construction, process pressure, and bolt fabrication.
Shaft sealing with a packed gland
This section discusses the use of compressed, stacked packing for shaft sealing. Topics covered include an explanation of how packing works, what to consider when using packing, good installation practices, and commissioning shaft packing. Keywords: lantern ring, leakage, lubrication, stuffing box, valve stem.
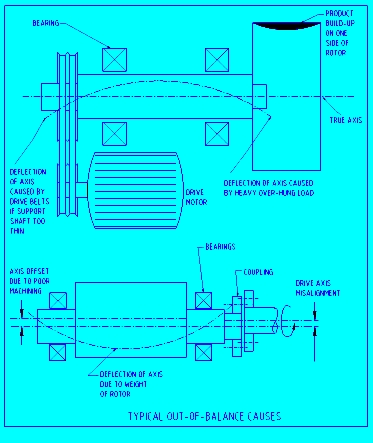
Vibration and out-of-balance equipment
Vibration from out-of-balance rotating equipment can be frightening. The ground shakes, machines jump about, hold down bolts come loose and parts break. An unbalanced rotating body will produce forces on its bearings and transmit them throughout its structure and into the foundations.
Get mechanical seals working properly
Mechanical seals are used to keep the bulk contents of rotating equipment such as pumps and compressors from escaping. They do this by sealing the shaft that protrudes from the casing. They require quality installation and operation conditions for long life.
Effects of centrifugal pumps on right end of pump curve
Pumps are designed and selected to operate near their highest efficiency point. If they operate at the right-hand end of the pump curve the likelihood of cavitation increases.
Net positive suction head
Pumps cavitate and run dry when the pressure leading into them falls below the vapor pressure of what they are pumping. At the vapor pressure, the liquid boils into a vapor and the liquid never reaches the pump. In order to know that the pressure to a pump is always above the vapor pressure, it is necessary to calculate that the pressure losses from pipe friction and suction lift will not cause the pressure to drop under the vapor pressure. The presence of dissolved gas in the liquid complicates the problem.
Vibration and its control
Vibration in equipment is the result of unbalanced forces. Out-of-balance is corrected by adding or removing material so that when the equipment is operating the unbalance is controlled to an acceptable level.
Corrosion in agitated conditions
Chemical corrosion occurs at increased rates in agitated conditions. Agitated conditions include stirred vessels and tanks, mixers and agitators, pumps, pipelines, and valves.
The importance of fit, tolerance, and clearance
Many equipment breakdowns and stoppages occur because of improper sizing between holes and shafts. The shaft is too tight in the hole; the hole is off-center; one part is loose on another and slips out of place or does not seal as it should.
Shaft alignment on pumps
Shaft misalignment is one of the most common reasons for bearing and mechanical seal failures. Rotating misaligned shafts produce vibration and complex fluctuating radial and axial loads that lead to breakdowns. Shaft alignment is a precision maintenance requirement that requires exacting care and detail and if not performed will cause much production downtime.
Shaft coupling selection issues
Shaft couplings are used between shafts to connect them so power can be transmitted and to allow for axial expansion. Shafts can either be aligned or intentionally inclined at an angle to each other. When at an angle a universal joint is used to connect the shafts. When directly aligned a shaft coupling is fitted.
Centrifugal pump cavitation
Cavitation in pumps is the presence of collapsing gas bubbles in a liquid stream. Under very low-pressure conditions the liquid vaporizes and boils. The gas bubbles collapse when they enter a region of high pressure. It is often heard as a rumbling sound coming from the pump. The collapsing bubbles cause mini-implosions that tear metal out from impellers and volutes.
Centrifugal pump life extension - the volute
Centrifugal pump life extension, the volute. The volute contains the process media while supporting the inlet and outlet nozzles and the bearing housing. The volute houses the spinning impeller and though it is stationary the flow and motion of the product across it caused by the impeller can lead to failures.
Effect of process changes on electric motors
Effect of process changes on electric motors. This section explains the effect of changing process loads on AC induction electric motor performance. The motor's behavior is a response to the load imposed on it by the equipment connected to it. The equipment's behavior is itself a response to the duty and service it has to perform. Where the equipment duty and service are adjustable by the operator or fluctuate as the process changes, the motor will react to those changes. When the changes are so excessive that they are beyond the motor's ability to handle them the motor stops and the equipment or process stops with it.
Pump life extension - the impeller
Pump life extension, the impeller. A spinning pump impeller provides the means to draw incoming product through the pump, energize it, and then force it out under pressure. The impeller converts the electrical energy from the motor into the hydraulic energy of the liquid. It does this by taking the liquid into the center of the impeller and flinging it outward at high speed. To efficiently continue to do this the impeller must remain in the same condition as it was when first installed. If the impeller deteriorates the conversion from electrical to hydraulic energy becomes inefficient. Power is wasted, flow and pressure fall and the pump cannot do its designed duty.
If you have a centrifugal pump problem, find the solution in Centrifugal Pump Problems & Answers today!
![]() Download right away in a printable PDF format!
Download right away in a printable PDF format!
$15.00
An Excerpt From Centrifugal Pump Problems & Answers
"CENTRIFUGAL PUMP CAVITATION"
Cavitation in pumps is the presence of collapsing gas bubbles in a liquid stream. Under very low pressure conditions the liquid vaporizes and boils. The gas bubbles collapse when they enter a region of high pressure. It is often heard as a rumbling sound coming from the pump. The collapsing bubbles cause mini-implosions that tear metal out from impellers and volutes.
Cavitation becomes a problem when the bubbles cause damage to internal parts from implosions as the pressure again increases or when the vapor bubbles block off the available liquid flow area and reduce capacity.
Sample from Centrifugal Pump Problems & Answers: Effect of Process Changes on Electric Motors
Need more information on pumps? Download the Complete Pumping white paper Set!
Please contact us with any questions.
