Corrosion Control Engineering
Corrosion Control Engineering for Beginners PDF
By Mike Sondalini

Corrosion Control Engineering for Beginners focuses mainly on the types of corrosion and types of corrosion prevention methods. A corrosive chemicals chart is included too. By knowing the basics, you will have a better understanding of the benefits of corrosion control. 21 pages.
Corrosion in agitated conditions is rarely discussed in other related material, but Mike has it covered here. He also has a section on chemical coatings, polyethylene, and fiberglass as they are corrosion control resources for some types of corrosion prevention methods. The layman may not be aware that stress increases metal corrosion, so mike covers it too.
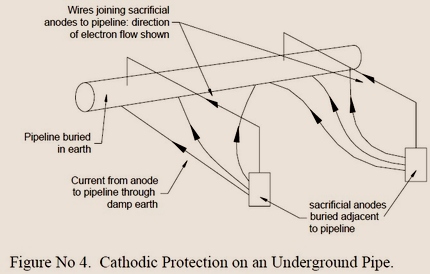
Alternatively, a metered electrical current from a power source can be connected to the cathode to supply the electrons. Figure 4 shows cathodic protection installed on a below-ground pipeline using sacrificial anodes that require regular replacement as they will corrode away.
Corrosion Control Engineering for Beginners PDF - Contents:
Types of metal corrosion and prevention.
The section explains the metal corrosion process including the basic chemistry of how metal loss occurs. Methods to control corrosion are also listed and explained. Metal corrosion is a chemical reaction between a metal surface and its environment. Corrosion can occur in a gaseous (dry) environment or a damp (wet) environment. It is the result of an electrical process in which electrons are exchanged between the corroding metal atoms and the acceptor element atoms. Corrosion control involves stopping or minimizing the loss of electrons between the components involved in the process.
Corrosive chemicals and chart.
Chemical corrosion can destroy the containment materials in contact with a process. Means exist to mitigate and even prevent chemical corrosion.
Corrosion in agitated conditions.
Chemical corrosion occurs at increased rates in agitated conditions. Agitated conditions include stirred vessels and tanks, mixers and agitators, pumps, pipelines, and valves.
Prevent corrosion with chemical coatings.
Coatings provide the industry with low-cost solutions to difficult chemical corrosion problems. This section covers the use of rubber, fiberglass, and epoxy linings.
Fiberglass construction to prevent corrosion.
Fiberglass is a glass fiber-reinforced plastic composite with excellent chemical resistance properties. Its physical properties, selection of resins and glass, method of construction and fabrication, and peculiar repair requirements must be appreciated when using this material.
Reducing wear in abrasive conditions.
Abrasion is the removal of material from a surface by the movement of material across its surface. The factors affecting abrasive wear are the surface properties of the item being worn away, the abrasive properties of the material moving across the surface, and the characteristics of motion. Where abrasive wear is a problem it becomes necessary to understand the mechanism of attrition.
Stress increases metal corrosion.
Too much stress in metal will cause it to fail. Failure can occur by putting the metal under a once-only load greater than it can take or by metal fatigue from continually loading the metal cyclically with a high load less than the breaking load. Stress produces strain at the molecular level in the metal and discontinuities between atoms come together to form microscopic cracks. Under continued stress, the cracks grow, and eventually the metal parts.
Polyethylene in corrosion control.
Polyethylene is one of the most commonly used engineering plastics. Its chemical resistance properties and ease of fabrication make it popular in the chemical industries. Its molecular structure provides the key to its versatility.
Gain valuable insight and understanding; get your copy of Corrosion Control Engineering for Beginners PDF today!
![]() Download right away in a printable PDF format!
Download right away in a printable PDF format!
$12.50
An Excerpt From Corrosion Control Engineering for Beginners PDF
"CONSIDER PROCESS CONDITIONS"
Using corrosion tables without considering all the process conditions can lead to poor materials selection. Most published data on compatibility do not take into effect agitated conditions. Some data only applies to ambient temperatures. Data is normally not available on the effect of aeration. Nor is data readily available on the effect of other contaminants, for example, chlorides with stainless steel.
In uncertain or changeable situations that will occur in a vessel consult the material manufacturer and ask for their advice. If they cannot help, then the only remaining option is to conduct your own laboratory tests or field trials. The chemical compatibility table below was derived from numerous published data. The most conservative temperatures were selected. Where no temperatures are shown ambient conditions apply.
Please contact us with any questions.
