Management Concepts and Ideas: Ian Sutton
A FREE EBook to compliment the EBooks below by Ian Sutton.
Back to main page for author Ian Sutton.
| Management Concepts and Ideas ... |
| This free eBook provides four simple examples to illustrate many of the concepts and ideas discussed in Ian Sutton's series of eBooks. You can download a full copy at no cost by right-clicking Management Concepts and Ideas, then select 'Save Target As'. |
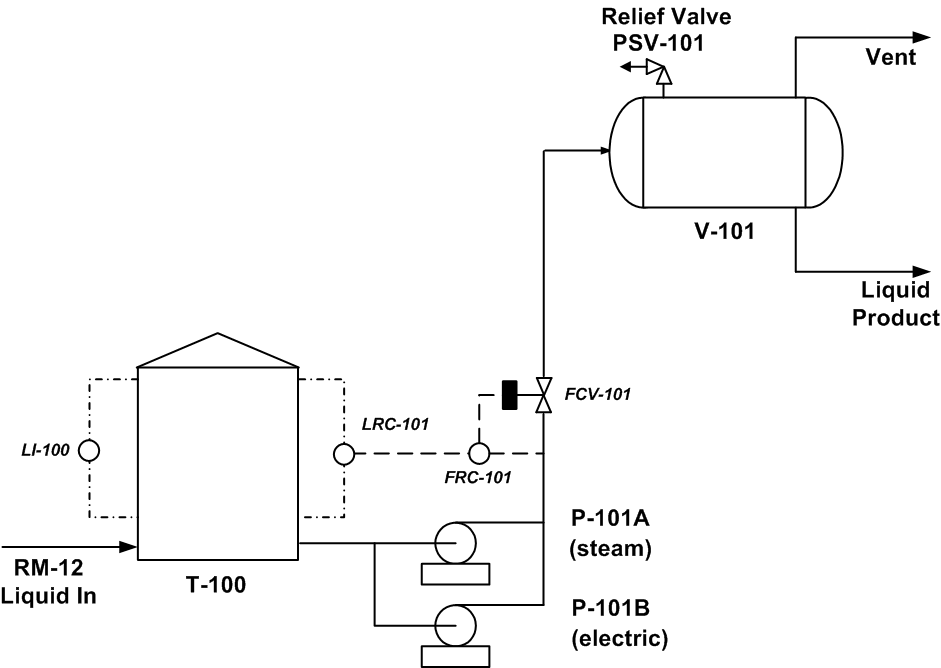
Example 1: Process FlowThe first example shows a simple process involving the flow of liquid from a tank into a pressure vessel. It illustrates the principles and techniques of process hazard analysis. Figure 1 Example 2: EquipmentThe second example concerns an equipment item widely used throughout the process industries: a shell and tube heat exchanger. It illustrates equipment failure analysis techniques, particularly Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA). Figure 2 Image in download Example 3: OperationsFigure 3 shows a forced-draft cooling tower. Warm water from the users enters at the top of the tower and then flows down the packing into the basin. The fans at the top of the tower pull air into the base of the tower. The air flows counter currently against the warm water. Some of the air evaporates, thus cooling the water. The cooled water is pumped to the users. Makeup water and treatment chemicals are added, as shown.
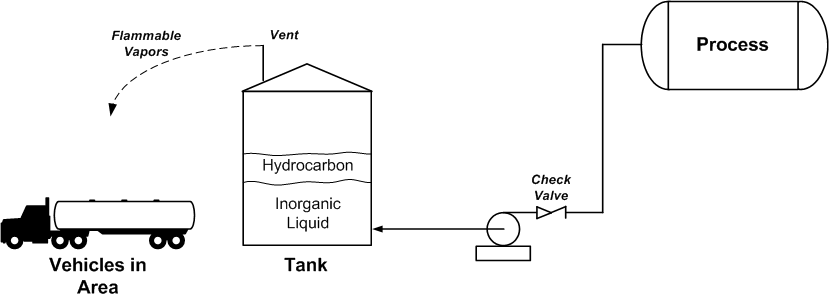
This example is used to illustrate the development of operating and maintenance procedures. Figure 3 Image in download Example 4: Management WorkflowThe fourth example illustrates the development and use of risk management systems. Figure 4 Image in download Example 5: Significant Potential IncidentA cone-roof atmospheric storage tank stores a nonflammable, low-vapor pressure inorganic liquid. The vapor space above the chemical is air; the tank breathes in and out through a simple vent line, as shown in Figure 5. Also shown is a vehicle; one of the facility roads runs close to the tank. A fairly steady stream of vehicles uses the road. The fifth and final example illustrates the development and use of risk management systems.
The pump stopped operating, the check valve failed to hold and light hydrocarbons flowed backward into the tank. A layer of hydrocarbons formed on top of the inorganic liquid, as shown. Figure 5
The hydrocarbons in the tank vaporized and then vented to the atmosphere, as shown. A hydrocarbon detector located about 100 meters from the tank detected the presence of flammable vapors.
The vapors did not light off. However, the potential for a serious event is high; the vapors could have ignited at a vehicle engine. The flame front could have entered the tank and caused the vapors to explode.
Table of ContentsIntroduction |
Please contact BIN95 with your questions and comments.