Industrial Heat Exchanger Design
Industrial Heat Exchanger Design and Usage PDF
By Mike Sondalini

Industrial Heat Exchanger Design PDF is great for maintenance and engineering students starting out. For those new to this subject, Mike explains heat transfer basics and heat exchanger design and use; and touches on Temperature sensing elements. Discussed are steam, boiler, heat exchanger, and water cooling towers. 17 pages.
Mike uses a couple of water cooling tower designs as a water to air heat exchanger example. Covered are fired packaged boiler heat exchanger, applied to cooling tower is also an example of heat exchanger cleaning.
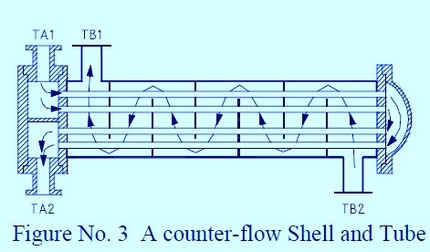
Figure No. 3 shows a counter-flow shell and tube heat exchanger with the corresponding points at which the temperatures are taken for the relevant graph in Figure No 1. If condensing steam (or gas), or a boiling liquid were on one side of the heat exchanger then the temperature on that side stays constant and the line on the graphs would be straight.
Industrial Heat Exchanger Design PDF - Contents:
Heat transfer basics.
Heat is energy and its nature is to flow from a state of high excitement to one of low excitement. Heat is transferred from a hot place to a cold place by convection, conduction, or radiation. This section explains the three modes of heat transfer and provides simple examples of each. Methods to reduce and increase heat transfer are also presented.
Heat exchanger design & use.
The section introduces readers to heat transfer in heat exchangers. It explains the concepts of temperature gradients across walls and parallel-current and counter-current flows. Both shell-and-tube and plate heat exchanges are discussed along with their common operational problems and remedies.
Temperature sensing elements.
The temperature of a process is an important measure to know as it indicates whether or not the process is in control. When high temperatures exist and accurate measurements are needed thermocouples and Resistance Thermal Devices (RTD) are two commonly used industrial temperature sensing methods.
Fired packaged boiler basics.
Steam boilers not used for power generation and of smaller size and energy output are termed packaged boilers. The heat source is usually either electric coils or burning fuel. When a flame is used to heat the water it is known as a fired packaged boiler. Fired boilers are considered efficient steam generators with about 85% of the available energy converted to steam. They can be of water-tube or fire-tube design. Boilers incorporate many key aspects of heat transfer to create steam from water. This section describes how fired boilers work and their key components.
Steam trap operation and selection.
The section covers the operation of steam traps and how they work. Their duty is to remove condensate from steam piping to ensure only vapor is sent through the pipeline. Steam is a greatly used medium in the industry. Its use ranges from heating processes and domestic fluids to driving turbines by the expansion of the vapor. Yet the steam trap at the bottom of a drop leg is easily forgotten.
Heating liquids by steam sparging.
Steam is often used for heating liquids. The direct steam injection into the process is known as steam sparging. The sparge design and location affect the efficiency of the process.
Water cooling tower design, operation and use.
There are two types of cooling water towers: natural draft and mechanical draft. A cooling water tower is used to remove heat from incoming hot water and reduce it to a lower temperature. It does that by evaporating off some of the hot water. The evaporated water takes away the heat. Exactly the same process occurs when your body sweets to keep you cool. You cool off even faster if there is a breeze blowing.
Water hammer and its control.
When a control valve or manual valve is shut fast in a full pipeline of moving liquid, the liquid comes to a sudden stop. If the pipe suddenly starts banging and thrashing about you can be sure a water hammer was created. A water hammer can cause great noise and damage. The pressure surge can deform pipes and valves and start leaks.
Gain valuable insight and understanding; get your copy of Industrial Heat Exchanger Design PDF today!
![]() Download right away in a printable PDF format!
Download right away in a printable PDF format!
$12.50
An Excerpt From Industrial Heat Exchanger Design PDF
"Cleanliness and Water Treatment" (heat exchanger cleaning)
A cooling tower is a great example of an industrial heat exchanger water air combination (air heat exchanger). Bacteria and algae grow in the water cooling tower's warm waters and wet crevices. Legionnaire Disease is the most famous illness that is associated with water cooling towers but there numerous different bacteria that have been found in water cooling towers. Cleanliness standards and procedures have been developed by health organizations for the care of cooling towers and tower owners and users are obliged to meet these requirements.
Typically a standard requires bacteria counts per volume of water to be less than a maximum number. The control of bacteria levels is usually done by the use of chemical biocides dosed into the tower. The biocides can be slug dosed or metered in by the pump. The standard also specifies water cleanliness and requires towers to be emptied and cleaned when dirt loads become excessive. A water bleed-off point is used to control the amount of dissolved solids build-up in the tower. In-line filters can also be installed in the piping circuit to keep the water clean for longer.
You may also be interested in our Heat Exchanger Certificate Course.
Please contact us with any questions.
