Electric Motor Current Protection
- Home >
- articles >
- electrical >
- engineering >
- motor curent protection
The effect of process changes on electric motors.

Much equipment failure comes from simple mistakes. These are sometimes due to forgetfulness, shortcuts, and ignorance. This results in the destruction of plant equipment at significant cost and inconvenience. At a low cost, you can protect against under and over currents for an electric motor-driven plant. It protects the motor from running beyond its design limits. The electricians place a current transformer around the electrical cables leading to the motor. The transformer connects to a monitoring device. It alarms when the current is outside the set limits.
ELECTRIC MOTOR CURRENT DRAW
The power to run a 3-phase induction electric motor depends on the motor's torque load. Low load means low power draw and low current draw. High load leads to high power draw and over current draw. Low load means the motor turns near full speed and does little work. It draws little power. High load means the motor is turning slower and working hard. It causes a more significant power draw. Overload means the motor has too much load and cannot turn at all.
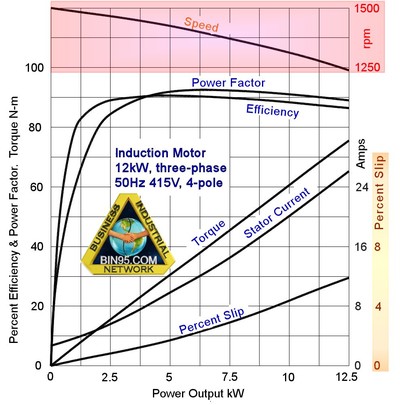
The stator current draw is an excellent variable to watch. It helps decide whether to stop the motor before it gets damaged. Anything attached to the motor will also stop. In this way, two conditions do not damage the equipment. One is a low-power draw. The other is a high-power draw.
DETECTING CHANGING ELECTRIC CURRENT
When an electric current flows through a wire, it produces a magnetic field around it. The greater the current, the stronger the magnetic field. The magnetic field will create electrical fields. It will cause current to flow in nearby wires. This phenomenon causes problems for Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC) and field equipment communications. The magnetic fields can interrupt signals between equipment and computers. In this case, communication cabling requires special shielding from the power cabling. However, this phenomenon helps an amp-meter measure the electric power draw.
By installing a current transformer on a power cable, the transformer gets its own current from the cable. The transformer current is proportional to the monitored cable current. Using a current transformer means there are no wires to cut. The transformer offers an affordable solution, is widely accessible, and simplifies installation. When coupled with a metering relay and a timer, it is possible to turn off the power to a motor when the current goes outside and set limits for a given period of time. Maintenance or the installer sets the limits. They set them for the current draw in the most and least demanding situations. When the current reaches its limits, the motor turns off. This protects it from abnormal loads.
The use of a current transformer is but one way to detect the presence of an electrical current. Other methods are available for under and over current detection. They include installing the monitoring device in series with the circuit.
UNDER-CURRENT SITUATIONS
When a motor is freewheeling or lightly loaded, the current needed to turn it is only a tiny fraction of the full load current. If this happens while a motor runs, something abnormal likely causes it.
This often happens with centrifugal pumps. They are deadheaded against a closed discharge valve. Or if a downstream suction valve is shut and the pump is cavitating because it is starved of liquid. In this case, the motor under current protection would detect the low load on the motor and turn it off. If the pump had a mechanical seal, it would be protected from damage before loss of lubricating fluid across the seal faces destroys the seal. Another example of where the motor under current protection would help is detecting unloaded conveyors or bucket elevators.
After a period of time, they could automatically turn off. When parts in a drive train fail, like the shaft coupling breaking, a drive shaft breaking, or drive belts coming off or snapping, the motor load drops. The drop in load current could trigger a shutdown and/or an alarm.
OVER CURRENT AND OVERLOAD SITUATIONS
As the load on an electric motor increases, the spinning rotor starts to slip more and slow down. The electric current draw rises as the motor tries to maintain its speed. The higher current flow causes more heat to develop inside the motor. Without over current detected, the heat builds up and can destroy the motor's internals. Being overloaded causes the motor to fail. Again, you can use over current detection to shut down the motor, protect it, and/or raise an alarm.
Overloads are likely in bulk materials handling situations. These include bucket elevators and screw feeders. Sudden overloads should be expected when equipment has to combat a dragging, digging, or scraping action as part of the process. The original designers should incorporate overload protection into the original design. Compensation for electric motor starting current is an obvious concern. But, it is also critical to watch the motor inrush current. It can vary with load.
ALLOW FOR THE OPERATING REQUIREMENTS
There are times when motors are required to freewheel for a short period, or there will be a short, temporary overload situation. In this case, a pump sending liquid into one tank must redirect the flow to a different tank. For a short period, the valves for both tanks may be closed. It is often better to keep the pump running for a few seconds against a deadhead rather than to put it off and restart it. In this case, the motor current will intentionally drop low. But, it does not want the undercurrent protection to stop the motor.
A timer stops the motor from shutting down prematurely in error. Observe the regular operating duty current draws and delays to permit normal operation, including the electric motor starting current. Delays like motor inrush current at start-up are set into the timer. The under or over current protection only activates after the timer counts out in the presence of abnormal loads.
There is one issue to be wary of when using current protection. It is possible to have a 'false' load on the motor. The current stays within the allowed band. This happens as long as a motor has 'normal' loads. Should this load result from a part failing, e.g., a collapsed bearing or a slipping vee-belt, then the current could still be in its working band, and the protection will not operate.
Current protection is a cheap and simple way to shield your equipment. It guards against errors that you could not foresee.
HIGH GEARING RATIOS
Current detection on highly geared drives (above about 50:1) tends to become insensitive to sudden changes in load. When the load changes unexpectedly, it goes through the drive to the motor. This reduces the torque a lot. The motor current will eventually affect the motor current detected, but it may not last long enough to trigger the protective systems. The designer can solve the problem. They can do this by adding torque detection to the load protection method.
The Variable Speed Drive (VSD) detects and controls torque, current, voltage, and shaft speed. This lets it control loads on high-geared drives. If unplanned load conditions occur, they can be lessened using electronics. You can also speed them up or stop them.
This article is a section from the "Process Control and Instrumentation Simplified" PDF download.
Related Courses:
Motor Controls Certificate Course
Motor Control Centers Online Course
Electrical Troubleshooting Training Course
Related Article:
Electric Motor Load Testing: The Effect Of Process Changes On Electric Motors
What do the letters FLA on a motor nameplate stand for?

